Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index (FLIPI). Online calculator
Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index (FLIPI) estimates overall survival based on clinical information.
FLIPI is designed to be used in patients with follicular lymphoma and to risk stratify patients based on prognosis. This can help guide when and how to treat such patients.
The FLIPI score was developed based on 4,167 patients with follicular lymphoma providing characteristics at diagnosis. Univariate and multivariate analyses were then used to develop a prognostic index. This was then validated in a cohort of 919 patients. Age, Ann Arbor stage, hemoglobin level, number of nodal areas, and serum LDH level were identified as adverse prognostic factors. The FLIPI was validated in a subsequent study and the performance improved by further stratifying age and including the presence of cerebrovascular disease.
The FLIPI, while a useful general prognostic tool, does not reliably predict those at diagnosis who will have an extremely rapid decline. Rather it assists with providing prognostic information. Ultimately, clinical judgement and comprehensive review of the patient’s previous workup are critical to make this assessment.
The GELF Criteria can help identify those patients with follicular lymphoma at higher risk for rapid disease progression and in whom immediate therapy may be needed.
The FLIPI score is easy to use with information most providers will already have available. Clinical evaluation, laboratory testing, and imaging are all that is needed to risk stratify patients and estimate prognosis.
| Age > 60 years | No | 0 |
| Yes | +1 | |
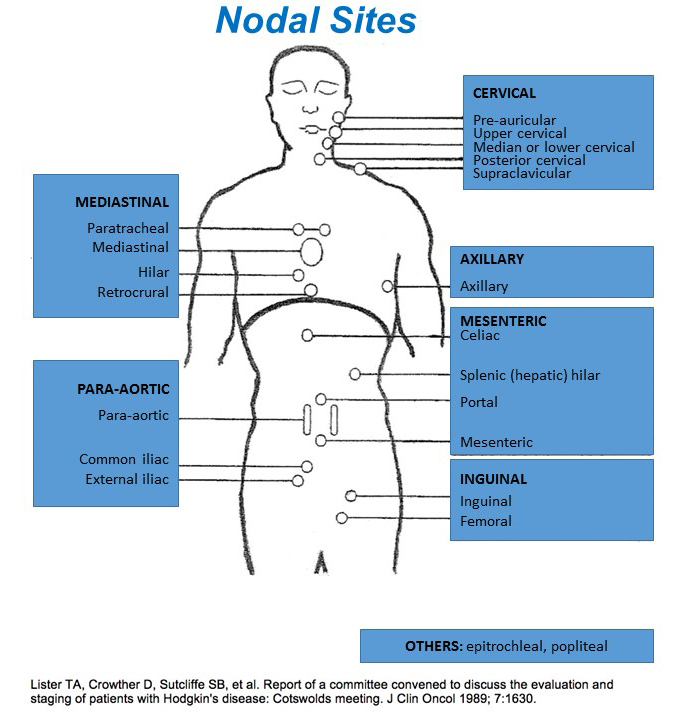
| >4 nodal sites See Nodal Sites diagram | No | 0 |
| Yes | +1 | |
| LDH elevated | No | 0 |
| Yes | +1 | |
| Hemoglobin <120 g/L or 12 g/dL | No | 0 |
| Yes | +1 | |
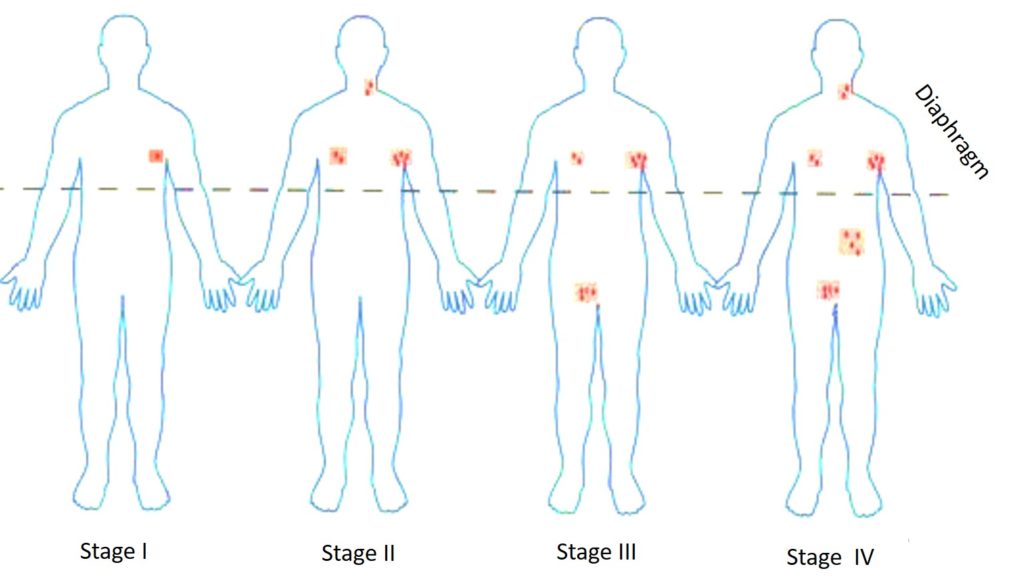
| Stage III-IV Stage I: disease is located in a single region, usually one lymph node and the surrounding area. Stage II: disease is located in two separate regions, an affected lymph node or organ and a second affected area. Both affected areas are confined to one side of the diaphragm. Stage III: disease involves both sides of the diaphragm, including one organ or area near the lymph nodes or the spleen. Stage IV: diffuse or disseminated involvement of one or more extranodal organs, with or without associated lymph node involvement. See Staging Diagram | No | 0 |
| Yes | +1 |
Score Interpetation
| Score | Risk Group | 10-year Overall Survival |
| ≤1 | Low | 70% |
| 2 | Intermediate | 50% |
| ≥3 | High | 35% |
Useful Mnemonic – NoLash
- Nodal areas
- LDH
- Age
- Stage
- Hemoglobin level
Nodal Sites
Staging Diagram
A FLIPI score of 0 to 1 is considered “low risk” with a 10 year overall survival of 70%. A score of 2 is considered “intermediate risk” with a 10 year overall survival of 50%. Finally, a score of ≥ 3 is considered “high risk” with a 10 year overall survival of 35%. Patients with an initial remission duration less than the median progression free survival for a particular treatment regimen and/or with a high FLIPI score are more likely to have a shorter remission duration.
Treatment is varied depending on the stage and tumor burden.
Stages I-II
- Treatment options include:
- Involved field radiotherapy (IFRT)
- Clinical trials
- Active surveillance
Stages III-IV or Bulky stage II – asymptomatic
- Treatment options include:
- Clinical trials
- Active surveillance
Stages III-IV or Bulky Stage II – with GELF/BNLI risk factors or high-risk FLIPI score
- Treatment options include:
- Rituximab + cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, prednisone
- Rituximab alone
- Bendamustine + rituximab
- Rituximab + cyclophosphamide, vincristine, prednisone
- Clinical trials
There is continued controversy around when and how to treat follicular lymphoma, including in patients with relapsed/refractory disease. Questions to consider when making treatment decisions:
- When to initiate therapy versus active surveillance
- Deciding amongst various treatment options
- Balancing efficacy and toxicities of treatment options
- Determining what constitutes a complete response/endpoint of treatment
- Finally, with follicular lymphoma, a provider should be aware of transformation to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, which is a more aggressive disease and would require prompt treatment.
Register on our website right now to have access to more learning materials!
Subscribe to our pages:
Literature:
- Solal-Celigny et al. Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index. Blood 104:1258-1265. (2004) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15126323/
- van de Schans SAM, et. al. Validation, revision and extension of the Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index (FLIPI) in a population-based settingAnn Oncol (2009) 20 (10): 1697-1702 first published online June 23, 2009 doi:10.1093/annonc/mdp053 https://www.journals.elsevier.com/annals-of-oncology
See also:
ClinCaseQuest Featured in SchoolAndCollegeListings Directory
Exciting News Alert! We are thrilled to announce that ClinCaseQuest has been successfully added to…
We presented our experience at AMEE 2023
AMEE 2023 took place from 26-30 August 2023 at the Scottish Event Campus (SEC), Glasgow,…
We are on HealthySimulation – world’s premier Healthcare Simulation resource website
We are thrilled to announce that our Simulation Training Platform “ClinCaseQuest” has been featured on…
Baseline Cardiovascular Risk Assessment in Cancer Patients Scheduled to Receive Cardiotoxic Cancer Therapies (Anthracycline Chemotherapy) – Online Calculator
Baseline cardiovascular risk assessment in cancer patients scheduled to receive cardiotoxic cancer therapies (Anthracycline Chemotherapy)…
National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) – Online calculator
The National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) is a scale designed to assess the…
SESAM 2023 Annual Conference
We are at SESAM 2023 with oral presentation “Stage Debriefing in Simulation Training in Medical…