Groupe d’Etude des Lymphomes Folliculaires (GELF) Criteria. Online calculator
Groupe d’Etude des Lymphomes Folliculaires (GELF) Criteria determines if immediate therapy for follicular lymphoma is required.
The criteria can help identify those patients with follicular lymphoma at higher risk for rapid disease progression and in whom immediate therapy may be needed.
Yes
No
Yes
No
Yes
No
Yes
No
Yes
No
Yes
No
Yes
No
Yes
No
| Number of criteria | Feasibility of GELF criteria | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Number of criteria | Feasibility of GELF criteria | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
This tool is best used as an instantaneous assessment of a patient’s disease burden. Ultimately, clinical judgement and comprehensive review of the patient’s previous workup are critical to make this assessment.
For overall prognosis, the FLIPI can risk stratify further than the GELF criteria.
The GELF criteria is easy to use with information most providers will already have available. Clinical evaluation, laboratory testing, and imaging are all that is needed to determine who has a high tumor burden based on the GELF criteria.
| Any nodal or extranodal tumor mass >7 cm diameter | No | 0 |
| Yes | +1 | |
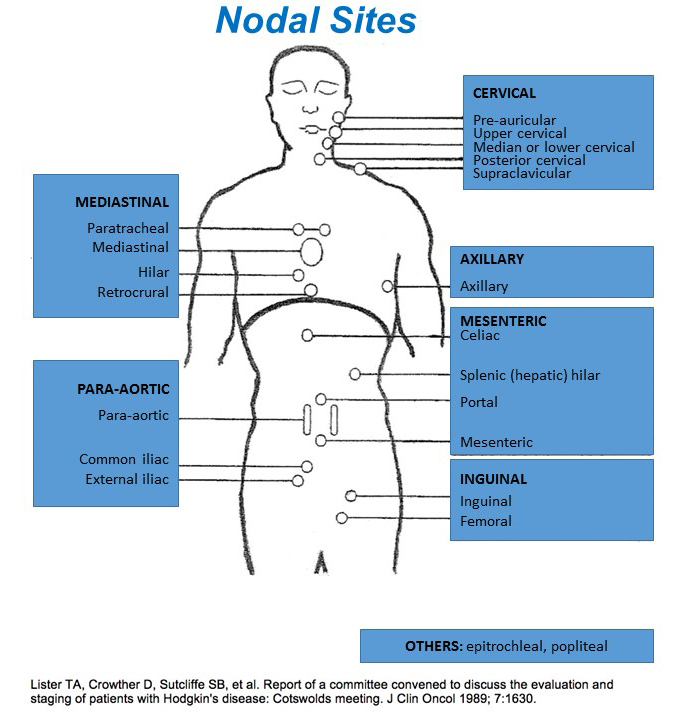
| Involvement of at least 3 nodal sites, each with diameter >3 cm View more nodal site information in the Nodal Sites section | No | 0 |
| Yes | +1 | |
| Presence of any systemic or B symptoms | No | 0 |
| Yes | +1 | |
| Splenic enlargement with inferior margin below the umbilical line | No | 0 |
| Yes | +1 | |
| Compression syndrome (ureteral, orbital, gastrointestinal) | No | 0 |
| Yes | +1 | |
| Pleural or peritoneal serous effusion (irrespective of cell content) | No | 0 |
| Yes | +1 | |
| Leukemic phase (>5.0 x10⁹/L circulating malignant cells) | No | 0 |
| Yes | +1 | |
| Cytopenia (granulocyte count < 1.0×10⁹/L and/or platelets < 100×10⁹/L) | No | 0 |
| Yes | +1 |
FORMULA
Patients must meet ≥1 criteria to be considered “high” tumor burden.
Сriteria:
- Any nodal or extranodal tumor mass >7 cm diameter
- Involvement of at least 3 nodal sites, each with diameter >3 cm
- Presence of any systemic or B symptoms
- Splenic enlargement with inferior margin below the umbilical line
- Compression syndrome (ureteral, orbital, gastrointestinal)
- Pleural or peritoneal serous effusion (irrespective of cell content)
- Leukemic phase (>5.0 x109/L circulating malignant cells)
- Cytopenia (granulocyte count < 1.0 x109/L and/or platelets < 100×109/L)
Nodal Sites
Refer to the staging systems FLIPI and Lugano classification to assist with risk stratifying patients. The GELF criteria is a quick test to determine which patients should be monitored versus treated now.
MANAGEMENT
Treatment is varied depending on the stage and tumor burden.
Stages I-II
- Treatment options include:
- Involved field radiotherapy (IFRT)
- Clinical trials
- Active surveillance
Stages III-IV or Bulky Stage II – asymptomatic
- Treatment options include:
- Clinical trials
- Active surveillance
Stages III-IV or Bulky Stage II – with GELF/BNLI risk factors or high-risk FLIPI score
- Treatment options include:
- RiTUXimab + cyclophosphamide, vinCRIStine, DOXOrubicin, predniSONE
- RiTUXimab alone
- Bendamustine + riTUXimab
- RiTUXimab + cyclophosphamide, vinCRIStine, predniSONE
- Clinical trials
CRITICAL ACTIONS
There is continued controversy around when and how to treat follicular lymphoma, including in patients with relapsed/refractory disease. Questions to consider when making treatment decisions:
- When to initiate therapy versus active surveillance
- Deciding amongst various treatment options
- Balancing efficacy and toxicities of treatment options
- Determining what constitutes a complete response/endpoint of treatment
- Finally, with follicular lymphoma, a provider should be aware of transformation to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, which is a more aggressive disease and would require prompt treatment.
EVIDENCE APPRAISAL
The original study compared three different intervention arms: active surveillance until clinical progression, immediate treatment with an oral alkylating agent (prednimustine), or treatment with a biologic response modifier (interferon-alpha). 193 in total were enrolled. The overall response rate of deferred treatment was 70%, with prednimustine was 78%, and with interferon-alpha was 70%. Similarly, the overall survival time at 5 years was 78%, 70%, and 84%, respectively. This showed that delayed treatment was a viable option for such an indolent lymphoma. However, those with early progression warrant treatment sooner.
Register on our website right now to have access to more learning materials!
Subscribe to our pages:
LITERATURE
Brice P, Bastion Y, Lepage E, et al. Comparison in low-tumor-burden follicular lymphomas between an initial no-treatment policy, prednimustine, or interferon alfa: a randomized study from the Groupe d’Etude des Lymphomes Folliculaires. J Clin Oncol. 1997. 15:1110-7. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9060552/
Solal-Céligny P, Lepage E, Brousse N, Tendler CL, Brice P, Haïoun C, Gabarre J, Pignon B, Tertian G,Bouabdallah R, Rossi JF, Doyen C, Coiffier B. DOXOrubicin-containing regimen with or without interferon alfa-2b for advanced follicular lymphomas: final analysis of survival and toxicity in the Groupe https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9667247/
Baseline Cardiovascular Risk Assessment in Cancer Patients Scheduled to Receive Cardiotoxic Cancer Therapies (Anthracycline Chemotherapy) – Online Calculator
Baseline cardiovascular risk assessment in cancer patients scheduled to receive cardiotoxic cancer therapies (Anthracycline Chemotherapy)…
Multiple Myeloma Diagnostic Criteria – Online Calculator
Revised Multiple Myeloma International Staging System (R-ISS) Online Calculator
Revised Multiple Myeloma International Staging System (R-ISS) – prognostication tool for myeloma patients based on…
Multiple Myeloma International Staging System (ISS) Online Calculator
Multiple Myeloma International Staging System (ISS) prognosticates the severity of multiple myeloma based on routinely…
SAVED VTE Score
SAVED score for venous thromboembolism risk stratification in patients with multiple myeloma receiving immunomodulators. [ezfc…
IMPEDE VTE Score
IMPEDE score for venous thromboembolism risk stratification in patients with multiple myeloma receiving immunomodulators. [ezfc…